Integrating Mistral AI into a PHP project
Artificial intelligence is taking an increasingly important place in our daily lives as developers. Software makers are now embedding AI directly into their applications to add intelligence, enhance user experience, and make their apps more intuitive and efficient.
Today, a simple API call is enough to tap into the full power of AI. If someone had told me that twenty years ago…
In this tutorial, we’ll see how to use Mistral’s API by leveraging an agent I previously created on their platform https://mistral.ai/.
This is the agent we’ll query, and which I’ve already integrated into my PHP code correction tool: https://phphub.net/fixer/.
Mistral?
Mistral AI is a French startup (cocorico!) specializing in artificial intelligence. Founded in 2023 by former researchers from DeepMind, Meta, and other major players in the field, it quickly became one of the leading European names in generative AI.
Unlike OpenAI or Anthropic, Mistral releases some (but not all) of its language models for anyone to freely download, use, and adapt. Today, the company offers several models, each designed for a specific purpose.
For our code completion tool, we’ll use Codestral 25.01: an advanced code generation model optimized for completion, Fill-in-the-Middle (FIM), corrections, unit test generation, and much more.
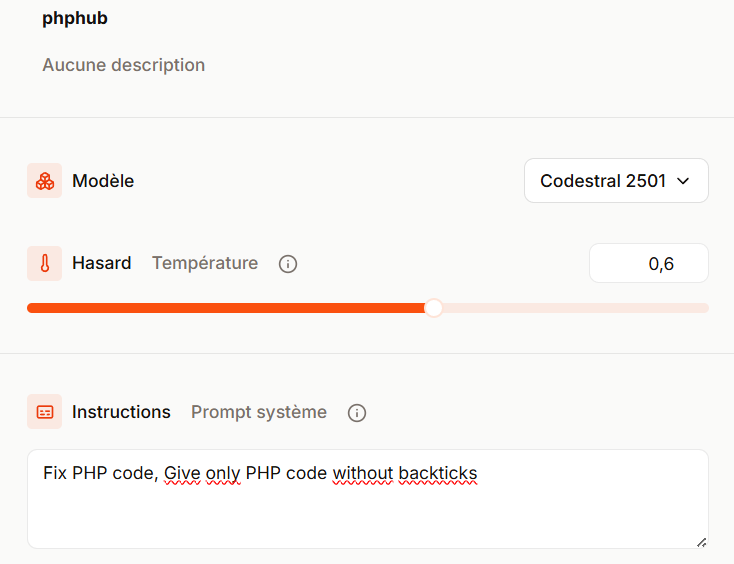
The agent
Creating an agent on Mistral is simple. You choose the model (here, Codestral 25.01) and define the system prompt, which in our case simply focuses on correcting PHP code.
Setting up connection information
To query the Mistral API, you need an API key. In our case, we also need the agent ID.
In this example, both pieces of information are stored in a secret.json file, which we load at the start of the script. This prevents exposing sensitive credentials directly in the source code—especially important if the project is hosted on GitHub ._.
{
"apiKey": "your_mistral_api_key",
"agentId": "your_agent_id"
}
In PHP, we start by loading this information and then preparing the headers required for the HTTP request. We specify the content type (JSON) and add the authentication token. Nothing surprising here!
$secret = json_decode(file_get_contents("./secret.json"));
$headers = [
"Content-Type: application/json",
"Authorization: Bearer ".$secret->apiKey
];
Building the message for the AI
The Mistral API works through message exchanges with a conversational agent.
In our case, we want to provide the AI with the code to correct, optionally accompanied by additional context (PHP error messages, notes, etc.).
The request body contains:
- the agent ID,
- a maximum token limit (to prevent excessive usage),
- and the list of messages to send.
$body = (object)[
"agent_id" => $secret->agentId,
"max_tokens" => 10000,
"messages" => [
(object)["role" => "user", "content" => "code:\n$source\n"]
]
];
if ($context != "") {
$body->messages[] = (object)[
"role" => "user",
"content" => "context:\n$context\n"
];
}
Here, this is specific to my needs: the $source variable contains the code to correct, while $context allows to provide additional instructions, for example specifying a particular coding style.
Sending the request with cURL
To communicate with the API, we use cURL, a well-known PHP extension often enabled by default, which allows us to make HTTP requests.
We send a POST request to Mistral’s agent completions endpoint, including the headers and the request body.
$ch = curl_init();
curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_URL, "https://api.mistral.ai/v1/agents/completions");
curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_HTTPHEADER, $headers);
curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_CUSTOMREQUEST, "POST");
curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_POSTFIELDS, json_encode($body));
curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_RETURNTRANSFER, true);
curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_HEADER, true);
$response = curl_exec($ch);
$http_code = curl_getinfo($ch, CURLINFO_HTTP_CODE);
$header_size = curl_getinfo($ch, CURLINFO_HEADER_SIZE);
$header = substr($response, 0, $header_size);
$body = substr($response, $header_size);
curl_close($ch);
This part of the code sends the request, retrieves the raw response, and then separates it into headers and body.
Interpreting the response
Once the response is received, we convert it into a PHP object using json_decode. The API typically provides several pieces of information, such as token usage and the AI-generated content.
In our case, we’re interested in the corrected text, which is found in the first choice returned.
$body = json_decode($body);
if ($body !== false) {
// token usage : $body->usage->total_tokens
// $body->choices[0]->message->content : corrected code
}
A concrete example
Let’s imagine we send this small piece of intentionally broken code:
<?php
echo "Hello world
The AI will understand that a closing quote and a semicolon are missing. It can then propose a correction like this:
<?php
echo "Hello world";
This corrected code is then returned to the application and can be displayed to the user.
Conclusion
In just a few dozen lines of PHP, we were able to query one of the AIs provided by Mistral. It’s simple and fast, even without being an AI expert.
The most interesting part is that the code is very similar for other AI providers: switching models or services usually only requires minor adjustments to the headers and API URL.
In just a few minutes, you can integrate the power of AI directly into your applications.